brachymetatarsia Tunisia
What is Brachymetatarsia ?
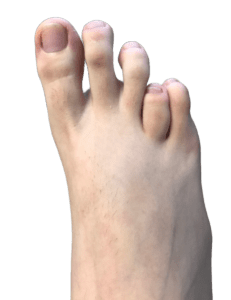 Brachymetatarsia is a medical condition in which one of the metatarsal bones, usually the fourth, is abnormally short. This can create an imbalance in the foot, affect gait and cause pain, skin thickening and shoe problems. Brachymetatarsia can be congenital or acquired and can be treated with shoe supports, braces, or surgery, depending on the severity of the condition.
Brachymetatarsia is a medical condition in which one of the metatarsal bones, usually the fourth, is abnormally short. This can create an imbalance in the foot, affect gait and cause pain, skin thickening and shoe problems. Brachymetatarsia can be congenital or acquired and can be treated with shoe supports, braces, or surgery, depending on the severity of the condition.
What are the causes ?
Brachymetatarsia is a rare congenital condition that affects the metatarsal bones, which are the bones that connect the toes to the rest of the foot. It is characterized by incomplete growth of one or more metatarsals, which leads to a decrease in the length of the bone and a disturbance in the alignment of the toes.
The exact causes of brachymetatarsia are still unknown, but genetic factors have been identified as being associated with this condition. It can be hereditary or occur spontaneously.
Brachymetatarsia can also be associated with other birth defects of the feet, such as equinus clubfoot varus, polydactyly, or missing toes.
Finally, certain traumas or infections can also lead to malformations of the metatarsal bones, which can cause secondary brachymetatarsia.
What are the symptoms ?
Symptoms of brachymetatarsia can vary depending on the degree and number of metatarsals affected. The most common signs of brachymetatarsia are:
A difference in the length of the toes, which can cause pain or difficulty in finding suitable shoes.
A deformity of the toes, which may tend to curl or overlap.
Forefoot instability, which can lead to malposition of the affected toe and pain when stepping. walking or running.
Difficulty bearing weight on the forefoot, which may cause a feeling of pain or instability .
Some patients with brachymetatarsia may have no symptoms, while others may have mild to severe symptoms. The severity of the symptoms often depends on the importance of the malformation and the age of the patient.
How to diagnose ?
The diagnosis of brachymetatarsia is usually based on a clinical examination and x-rays of the forefoot. Your doctor will examine your foot to determine if you have signs of brachymetatarsia, such as shortened toes or toe deformity. X-rays of the forefoot will confirm the diagnosis and determine the degree of the malformation.
In some cases, additional medical imaging, such as an MRI or computed tomography (CT), may be needed to assess the internal structures of the foot and confirm the diagnosis.
How to treat brachymetatarsia ?
The treatment of brachymetatarsia depends on the degree of the malformation and the associated symptoms. Here are some possible treatment options:
Orthotics and special shoes: If the brachymetatarsia is mild and does not cause pain or functional problems, foot orthotics or special shoes can help redistribute pressure on the foot and improve comfort and stability.
Surgery: If the brachymetatarsia is more severe and causes pain or difficulty bearing shoes, surgery may be required. The procedure involves lengthening the shortened bone, often using bone grafts or osteotomy techniques, which can be performed on an outpatient basis.
Cosmetic surgery: On the other hand, cosmetic treatment can be considered if the person patient with brachymetatarsia is concerned about the appearance of her feet.
What are the possible complications of brachymetatarsia ?
Brachymetatarsia can lead to several complications, including:
Pain: Brachymetatarsia can cause forefoot pain and affect walking and daily activities.
Toe deformity: Brachymetatarsia can lead to the development of toe deformities, such as hammer or claw toes .
Difficulty wearing shoes: Brachymetatarsia can make it difficult to wear comfortable, snug-fitting shoes, as the bone shortens may cause pressure and chafing.
Osteoarthritis: Untreated or poorly treated brachymetatarsia can lead to early forefoot osteoarthritis, which can cause more pain and deformity.
Back pain: Compensatory posture due to brachymetatarsia can cause back pain.
Is surgery an option to treat brachymetatarsia ?
Surgery is an option to treat brachymetatarsia if other treatments such as the use of orthopedic insoles or special shoes do not work.
Surgery may involve rebuilding the shortened bone, possibly with bone grafting or adding an implant to lengthen the bone. Depending on the extent of the brachymetatarsia, surgery may also include correction of any associated toe deformity.
What are the operational consequences ?
The postoperative course of surgery for brachymetatarsia depends on several factors, including the surgical technique used and the extent of the operation. Here are some things to consider:
Pain: You will likely feel some pain after the operation, but this can be controlled with pain medication prescribed by your doctor.
Immobilization: You will need to keep your foot immobilized for some time after the operation using a splint , a boot or a cast. This will allow the bone to heal properly.
Rehabilitation: You will need to perform rehabilitation exercises to improve your foot mobility and strength. Your doctor will let you know what exercises you need to do and when you can resume normal activity.
Infections: There is a risk of infections after surgery, so you will need to monitor your foot for any signs of infection. infection, such as excessive pain, redness or warmth.
Follow-up visits: You will need to return to your doctor for regular follow-up visits to monitor the healing of your foot and make sure there are no complications.
How long does it take to recover?
Recovery time after brachymetatarsia surgery can vary depending on many factors, such as the surgical technique used, severity of the condition, age, and overall health of the patient. In general, it takes about 6 to 8 weeks for the bone to heal and for the foot to fully recover. The first 2-3 weeks after the operation can be difficult, with pain and limited mobility, but it usually gets better after this initial period.
During the recovery period, it is important to follow your doctor's recommendations for postoperative care to promote rapid healing and avoid complications. You will need to rest and immobilize your foot as much as your doctor tells you to, as well as follow the progressive rehabilitation program to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility. Full recovery can take several months, depending on the starting condition and individual response to surgery.
Is it painful ?
Brachymetatarsia surgery can be painful for the first few days and weeks after surgery, especially during the initial recovery phase. Postoperative pain is normally manageable with painkillers prescribed by your doctor, but you may experience some discomfort and mild pain whenever you walk or move your foot during this time.
What are the advantages of surgery ?
Surgery to treat brachymetatarsia can have several benefits for patients. Here are some of the potential benefits of surgery:
Correcting the deformity: Surgery corrects the underlying structural problem that is causing the deformity. brachymetatarsia.
Improved Foot Aesthetics: Lengthening shortened bones can improve the appearance of the foot and body as a whole, which can help reduce self-consciousness and improve self-confidence.
Reduced Pain: For some patients, brachymetatarsia can lead to foot pain and inflammation that can be relieved following successful surgery.
Improved Functionality: By correcting the deformity, surgery can improve the ability to walk and move more more comfortable and natural, which can help prevent further foot problems.
Are there any associated complications ?
As with any surgery, there are risks of complications associated with the muscle implant. However, the risk of complications depends on many factors, including the complexity of the operation, the general health of the patient, and compliance with post-operative instructions.
Possible complications include infection, hematoma, muscle necrosis, implant rupture, muscle asymmetry, or abnormal scar formation. Although these complications are relatively rare, it is important to discuss the potential risks with your surgeon before deciding to have a procedure.
By following your surgeon's post-operative instructions, you can minimize the risk of complications and promote a smooth recovery. If you notice signs of infection or other problems, such as increased pain, fever, redness or swelling around the treated area, it is important to contact your surgeon promptly for help. 'aid.
Conclusion
In conclusion, brachymetatarsia surgery can help correct short toes, improving the appearance and functionality of the foot. However, as with any surgery, there are risks of complications to consider. It is therefore important to discuss the potential benefits and risks with your doctor before making an informed decision on the best treatment option for you.