Chondroma
What is a chondroma ?
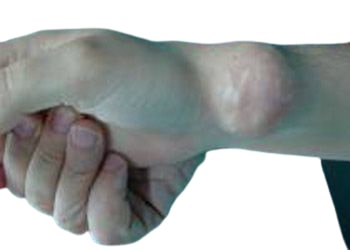 A chondroma is a benign cartilage tumor that often develops in bones and joints. Although considered non-cancerous tumors, chondromas can cause pain and loss of joint function in certain situations.
A chondroma is a benign cartilage tumor that often develops in bones and joints. Although considered non-cancerous tumors, chondromas can cause pain and loss of joint function in certain situations.
What are the causes ?
Chondromas are benign cartilage tumors that often develop in bones and joints. The exact causes of chondromas are unknown, but there are known risk factors.
Risk factors for chondromas include family history of chondromas and genetic disorders such as Ollier's disease and Maffucci's disease. Studies have also suggested that certain types of chondromas may be linked to chromosomal abnormalities and genetic mutations.
In rare cases, chondromas can be associated with systemic diseases such as Paget's disease, which is a bone disease characterized by increased and abnormal bone growth.
Chondromas can also develop due to exposure to environmental toxins, such as toxic chemicals and radiation.
What are the symptoms ?
Some people may experience symptoms associated with chondromas, which may include:
Pain: Chondromas located in the bones may cause a dull ache or a feeling of pressure in the affected area.
Swelling and Swelling: Chondromas in the joints can cause swelling and swelling, which may be accompanied by loss of joint function.
Limitation of movement: The presence of a chondroma in a joint can cause loss of mobility and limit the movements of the joint.
Feelings of locking or locking of the joint: Chondromas in a joint can cause feelings of locking or locking of the joint. locking in the joint.
Symptoms associated with chondromas can vary depending on the location of the tumor and its size. In some cases, chondromas may have no symptoms and be discovered accidentally during a medical examination.
How to diagnose ?
Diagnosing chondromas usually involves a combination of physical exams, medical imaging, and biopsy.
Physical Examination: The doctor checks the affected area for signs of pain, swelling, and limitation of movement .
X-rays: X-rays are often used to diagnose chondromas. X-rays can help identify changes in bone tissue, such as calcifications and changes in bone contour, which are telltale signs of a chondroma.
Computed tomography: Computed tomography, or CT, is an advanced X-ray imaging technique that can provide images in cross section of the affected region. CT can help visualize chondromas in more detail than standard x-rays.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Magnetic Resonance Imaging, or MRI, uses magnetic waves to create detailed images soft tissues of the affected area. MRI can be useful for evaluating chondromas located in surrounding soft tissues, such as joints.
Biopsy: In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis of chondroma. A biopsy involves removing a sample of tissue for microscopic examination to determine if the tumor is benign or malignant.
What are the treatment options ?
Treatment for chondromas depends on the size and location of the tumor and the severity of the symptoms. Treatment options for chondromas may include:
Observation: In some cases, observation may be recommended if the tumor is small and not causing symptoms. The doctor will monitor the growth of the tumor with regular exams and may recommend treatment if the tumor begins to cause symptoms.
Surgery: Surgery is usually the treatment of choice for chondromas that cause symptoms. The procedure involves completely removing the tumor, while preserving as much healthy tissue as possible. Surgery can be performed openly or arthroscopically, depending on the location of the tumor.
Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy may be used to treat chondromas that cannot be surgically removed, such as chondromas located in sensitive or critical areas that present a risk of nerve or functional damage.
Medications: Although there is no specific medication to treat chondromas, certain medications can be used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Commonly prescribed medications may include pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, and corticosteroids.
How is the surgery performed ?
Surgery is a common treatment option for chondromas that cause symptoms. The surgical procedure for a chondroma usually involves completely removing the tumor while preserving as much healthy tissue as possible. Here is an overview of the typical steps in surgery for a chondroma:
Anesthesia: The patient is usually asleep under general anesthesia for the procedure.
Incision: The surgeon will make an incision in the skin to access the tumor. The incision can be made open or arthroscopically, depending on the location of the tumor.
Chondroma removal: The surgeon will carefully remove the tumor to avoid damaging surrounding tissue. The procedure can take anywhere from a few minutes to several hours, depending on the size and location of the tumor.
Suturing the wound: Once the tumor has been removed, the surgeon will suture the wound and apply dressings to help reduce the risk of infection.
Post-operative care: The patient will be monitored closely in the hours following the operation to ensure that he is recovering correctly and that he does not present any complications.
What is the recovery period ?
The recovery period after chondroma surgery depends on several factors, such as the size and location of the tumor, post-operative complications, and the surgical methods used. In general, most patients can expect a total recovery period of several weeks to several months.
Immediately after the procedure, the patient will be monitored closely for any signs of excessive bleeding, infection, or other potential complications. If all goes well, the patient can go home the same day or the day after the operation.
Patients should expect to experience some pain and swelling in the area of the incision. Analgesic medications may be prescribed to help relieve the pain. It is also recommended that patients rest and avoid strenuous physical activity for a few weeks after the procedure to allow the body to heal.
Patients may undergo physical therapy to help restore function, strength, and flexibility to the affected area. Rehabilitation exercises may be prescribed to strengthen surrounding muscles and joints and help prevent complications.
What are the advantages ?
Surgical treatment of chondromas can offer several advantages to patients affected by this benign tumor. Here are some of the benefits of surgery for the treatment of chondromas:
Symptom relief: Surgery can help reduce or eliminate associated pain, swelling and movement limitations to chondromas.
Complete tumor removal: Surgery offers the possibility of completely removing the tumor, reducing the risk of recurrence ( recurrence) and promoting complete healing.
Low risk of complications: Surgery for chondromas is a common and safe procedure, with relatively low complication rates .
Improved quality of life: Surgery can help improve the quality of life of patients by allowing them to regain normal functionality of the affected area.
Personalized Recovery Plan: Patients can work closely with their doctor to develop a personalized recovery plan that is right for them. suits them best, based on their health status, needs and personal lifestyle.
Ultimately, surgery may provide several benefits to patients with chondromas by reducing symptoms, removing the tumor, and improving their quality of life. However, each case of chondroma is unique and the benefits of surgery may vary from patient to patient.
What are the risks and complications ?
Although surgery is a common and relatively safe method for treating chondromas, it also carries some risks and complications. Here are some of the possible risks and complications associated with chondroma surgery:
Infection: There is a potential risk of infection after surgery, which can lead to pain, redness and swelling. swelling in the affected area.
Excessive bleeding: Chondroma surgery can cause excessive bleeding during or after the operation, which may require a blood transfusion or further intervention.
Damage to surrounding tissues: Surgery can sometimes result in damage to surrounding tissues, which can lead to postoperative complications. operating.
Scarring: The scar may be visible depending on the location of the incision and may affect the physical appearance of the patient .
Anesthetic reaction: Patients may react to general anesthesia and experience side effects such as nausea, vomiting , dizziness or confusion.
Tumor recurrence: There is a potential risk that the tumor will come back (recur) after surgery.
Change in limb alignment: Depending on the location of the tumor, chondroma surgery can lead to a change limb alignment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, chondromas are benign cartilage tumors that can cause pain, swelling, and limitations in movement. Although chondromas are considered relatively uncommon, their diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment require specialized expertise.
Treatment for chondromas usually involves a combination of monitoring, surgery, radiation therapy, and taking medication. Surgery is often recommended if the tumor is causing symptoms, and it can provide several benefits, including symptom relief, complete tumor removal, and improved quality of life.