chondrosarcoma
What is a chondrosarcoma ?
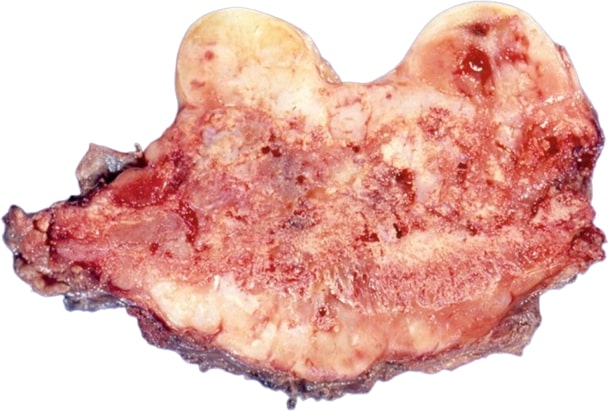 Chondrosarcoma is a malignant tumor that develops from the cartilage cells of the body. Chondrosarcoma can develop in many parts of the body, but it is most common in long bones, such as the femur, humerus, and tibia.
Chondrosarcoma is a malignant tumor that develops from the cartilage cells of the body. Chondrosarcoma can develop in many parts of the body, but it is most common in long bones, such as the femur, humerus, and tibia.
What are the causes ?
The exact causes of chondrosarcoma are still unknown. However, various studies have identified several factors that may increase the risk of developing chondrosarcoma.
Genetic factors: Genetic mutations can lead to the development of chondrosarcoma. Certain genetic conditions, such as Ollier's disease and Maffucci's disease, are also associated with an increased risk of developing chondrosarcoma.
Radiation exposure: Radiation exposure, especially during previous cancer treatment, can increase the risk of developing chondrosarcoma.
Age: Chondrosarcoma is most common in people over the age of 40.
Physical activity: certain types of physical activity, such as wrestling, may increase the risk to develop chondrosarcoma.
The presence of underlying medical conditions: conditions such as polyosteochondromatosis (POC) and cartilage dysplasia may increase the risk of developing chondrosarcoma.
What are the symptoms ?
Symptoms of chondrosarcoma can vary depending on the size and location of the tumor. People with chondrosarcoma may have no symptoms early in the disease. However, as the tumor grows, symptoms may include:
Pain: Pain is often an early symptom of chondrosarcoma. The pain may be constant or intermittent and may worsen at night.
Swelling: Swellings and lumps may form around the affected area. The affected area may also appear bulkier or thicker than other areas.
Spontaneous fracture: Spontaneous bone fractures can occur in the affected area without significant trauma.
Loss of mobility and function: The tumor may affect the ability of the affected joint to move or cause pain. stiffness, numbness or loss of sensation.
Fatigue, weight loss and fever: these symptoms can occur in more advanced cases, when the tumor has spread to other parts of the body.
How to diagnose ?
The diagnosis of chondrosarcoma begins with a thorough evaluation of the patient's symptoms and medical history. The doctor may also order several tests to detect the presence of the disease or to exclude other pathologies.
Here are some of the tests commonly used to diagnose chondrosarcoma:
X-rays: X-rays are often the first step in the diagnosis of chondrosarcoma. X-rays can reveal the presence of fractures or tumors in the bones.
Computed tomography (scanner) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): CT and MRI can visualize details of the tumor and determine its precise size and location.
Biopsy: Biopsy involves taking a sample of tissue from the affected area. This intervention confirms the diagnosis of chondrosarcoma and determines the category of the tumour.
Bone scan: A bone scan uses a radioactive substance to identify areas of unusual activity in the bones. It can help diagnose chondrosarcoma metastases.
Blood tests: Blood tests may be done to check for signs of the disease.
What are the treatment options ?
The treatment for chondrosarcoma depends on the size and location of the tumor, the quality of the cancer cells, the patient's age and general health.
Surgery: Surgery is often the first recommended treatment option for patients with chondrosarcoma. The goal of surgery is to completely remove the tumor. In some cases, a bone graft or prosthesis may be used to replace the removed bone tissue.
Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy x-rays to destroy cancer cells. Radiation therapy can be used before or after surgery, depending on the size and location of the tumor.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the use of anti-cancer drugs to destroy cancer cells. Chemotherapy can be used in combination with surgery or radiation therapy to treat chondrosarcoma.
Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy uses specific drugs to target cancer cells, disrupting the signals that allow them to grow and their expansion.
Monitoring: In some cases, chondrosarcoma tumors may not require immediate treatment, but patients may be monitored regularly to detect any changes in the size or growth of the tumour.
How is the surgery performed ?
Surgery is often the first treatment option for patients with chondrosarcoma. Surgery for chondrosarcoma is usually performed by an orthopedic surgeon who specializes in bone procedures.
This is how surgery for chondrosarcoma usually takes place:
Preparation: Before surgery, the patient will undergo preoperative examinations and tests to assess the degree spread of the tumor and the size of the affected area. The surgeon and medical team will discuss the procedure and post-operative care with the patient.
Anesthesia: The operation is usually performed under general anesthesia which means the patient will be asleep and unconscious for the entire the duration of the intervention.
The incision: once the patient is asleep, the surgeon will make an incision to access the tumor and surrounding tissues.
Excision: the surgeon will completely remove the tumor and a healthy margin of surrounding tissue to minimize the risk of spreading the tumor. If the tumor is located in a bone, the affected part of the bone may also be removed.
Reconstruction: In some cases, a bone graft or prosthesis may be used to replace the removed part of the bone.
Closure: Once the procedure is complete, the wound will be cleaned and closed. Drains may be placed in the affected area to prevent blood or fluid buildup.
Follow-up: The patient will be transported to an intensive care unit or recovery room to recover from anesthesia . Regular follow-up with the surgeon and the medical team will be necessary to ensure full recovery.
What is the recovery period ?
The recovery period after surgery for chondrosarcoma can vary depending on the size and stage of the tumor, the location of the tumor, and the age and general condition of the patient. In general, complete healing can take several months.
Here is an overview of what patients can expect during their recovery period:
Hospitalization: Patients may be hospitalized for several days after surgery to monitor their condition and stabilize the pain.
Rehabilitation: Physiotherapy and rehabilitation are often needed to help patients regain muscle strength, mobility and function. Patients should work with a physical therapist to develop a personalized rehabilitation plan.
Pain Control: Pain control is an essential part of post-operative recovery. Patients may be given analgesic medications to relieve pain.
Medical follow-up: Patients should follow a rigorous post-operative care plan, which may include regular check-ups to monitor healing of the wound and the early detection of signs of complications.
Return to work or activities: Most patients can return to normal daily activities after several weeks of recovery. Some patients may need a longer convalescence period or an adjustment to their working environment to facilitate their recovery.
What are the advantages ?
Chondrosarcoma treatment has significant benefits for patients, which can have positive outcomes and improved quality of life.
Here are some of the benefits of chondrosarcoma treatment:
Tumor removal: The main goal of treatment for chondrosarcoma is to completely remove the tumor. If the tumor is successfully removed, it can significantly reduce the risk of spreading the disease.
Improved Quality of Life: After treatment, patients can experience a significant improvement in their quality of life. Patients can recover their previous mobility and function and return to their general condition before diagnosis.
Preventing complications: Treating chondrosarcoma can help prevent complications from the disease, such as pain, bone fractures and loss of function.
Monitoring and treatment of metastases: In some cases, chondrosarcoma can spread to other parts of the body. If so, additional treatment such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy may be needed to treat the metastases.
Monitoring: Even after treatment is completed, patients should be monitored regularly to monitor disease progression and detect any changes.
What are the risks and complications ?
Here are some potential risks and complications associated with chondrosarcoma treatment:
Pain: Pain is a common side effect of surgery and post-operative recovery. Patients may need pain medication to relieve pain during the recovery period.
Infection: Surgery may increase the risk of infection. It is important for patients to follow post-operative care instructions provided by their medical team to minimize the risk of infection.
Injury to the nerves: Surgery for chondrosarcoma can lead to injury to the nerves, which can lead to pain, muscle weakness and loss of sensation.
Bleeding: During surgery there may be excessive bleeding which requires medical intervention to stop loss of blood. blood.
Lung Complications: Some surgeries can lead to lung complications, including pneumonia or pulmonary embolism.
Fracture of the bone: after surgery, some affected areas of the bone may be more fragile and be more prone to fracture.
Radiation therapy complications: side effects of radiation therapy may include fatigue, skin problems, nausea and vomiting.
Chemotherapy side effects: Chemotherapy side effects may include nausea, fatigue, vomiting, headaches and hair loss.
Conclusion
In conclusion, chondrosarcoma is a form of bone tissue cancer that can affect people of any age. Treatment options for chondrosarcoma may include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Although the treatment has significant benefits, it can come with risks and complications such as pain, infection, and bone fracture.