mastectomy
What is a mastectomy ?
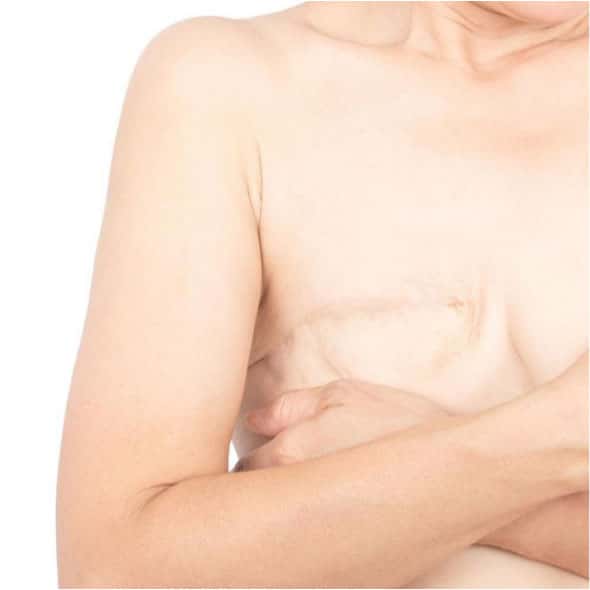 A mastectomy is an operation that involves the total or partial removal of a breast. This operation is frequently performed during the treatment or prevention of breast cancer. Mastectomy is divided into total mastectomy and partial mastectomy, depending on the extent of breast removal. Several elements can influence the decision for a mastectomy, such as the stage of the cancer, patient preferences, medical recommendations, and the need for additional treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
A mastectomy is an operation that involves the total or partial removal of a breast. This operation is frequently performed during the treatment or prevention of breast cancer. Mastectomy is divided into total mastectomy and partial mastectomy, depending on the extent of breast removal. Several elements can influence the decision for a mastectomy, such as the stage of the cancer, patient preferences, medical recommendations, and the need for additional treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
What is the difference between a partial and total mastectomy ?
Partial mastectomy, or lumpectomy, is a surgery aimed at removing the tumor while retaining the majority of the breast, thus preserving its shape and volume. This procedure is less invasive than total mastectomy, which involves the complete removal of the breast, including the areola, nipple, and thoracic muscle covering. It is often recommended for large tumors, situations where conservative surgery is not possible, or in the presence of multiple tumors in the same breast. In short, partial mastectomy removes the tumor while preserving the breast, while total mastectomy removes the entire breast.
What is the success rate of a partial mastectomy compared to a total mastectomy ?
The size and location of the tumor, the initial volume of the breast, the patient's general health and personal preferences are factors that influence the success rate of a partial mastectomy compared to a total mastectomy. The success rate of both procedures is high, with local recurrence estimated at around 5% after 10 years.
How long does recovery take after a partial or total mastectomy ?
Recovery after a partial or total mastectomy varies, usually lasting several weeks, and depends on factors such as the complexity of the operation and general health. Post-operatively, patients may require pain medication, a compression bra, and physical therapy. After a total mastectomy, additional care for scars and surgical drains is also necessary for approximately one to two weeks.
What are the options for breast reconstruction afterwards ?
After a mastectomy, breast reconstruction may be immediate or delayed, depending on the patient's preferences and health status. Options include prosthetic implantation, use of flaps such as the latissimus dorsi or DIEP, lipofilling, and areola and nipple reconstruction. Immediate reconstruction can reduce the number of surgical procedures, improve aesthetic results and provide psychological support, but the choice also depends on the type of cancer.
How to manage pain after a mastectomy ?
After a mastectomy, post-mastectomy pain syndrome (PMDS) and phantom breast pain are common complications. PMDS, caused by damaged nerves during surgery, can be treated with painkillers, transcutaneous nerve stimulation, capsaicin cream, massage, or Botox injections. Phantom breast pain, characterized by sensations of itching, tingling, or throbbing pain, may require medications, relaxation methods, and complementary therapies such as acupuncture or hypnotherapy. It is crucial to discuss treatment options with your medical team.
Are there alternatives to partial or total mastectomy for the treatment of breast cancer ?
Indeed, there are options for partial or total mastectomy to treat breast cancer. These options include conservative surgery, also known as a lumpectomy, which involves removing the tumor while preserving the rest of the breast. It is common to consider this approach for breast cancers detected at an early stage. Complementary treatments such as radiotherapy, chemotherapy or hormonal therapy can be combined with conservative surgery to remove remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence.
In summary
In summary, there are two main types of surgery for breast cancer: partial mastectomy, which removes the tumor while preserving the shape and volume of the breast, and total mastectomy, which removes the entire breast, including the breasts. breast tissues, nipple and areola. Partial mastectomy can cause asymmetries and deformities, with a risk of local recurrence. Total mastectomy can also lead to deformities, healing problems, loss of sensitivity and local recurrence.