Myomectomy - Removal of uterine fibroids
Definition
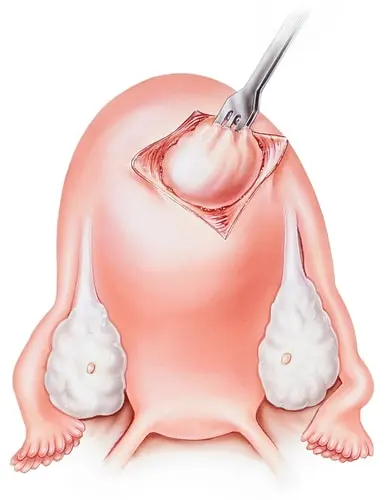 Myomectomy is a surgical procedure performed to remove uterine fibroids , very common benign tumors of childbearing age that develop inside or along the walls of the uterus. uterus, this cause is known as uterine myomatosis. Myomectomy is a safe and effective surgical treatment for the removal of fibroids, suitable for all women with severe symptoms, and always possible when the patient wishes to preserve the uterus.
Myomectomy is a surgical procedure performed to remove uterine fibroids , very common benign tumors of childbearing age that develop inside or along the walls of the uterus. uterus, this cause is known as uterine myomatosis. Myomectomy is a safe and effective surgical treatment for the removal of fibroids, suitable for all women with severe symptoms, and always possible when the patient wishes to preserve the uterus.
When is it necessary to perform a myomectomy?
Uterine fibroids, also called fibroids or leiomyomas, may be asymptomatic and go unnoticed or, depending on their size and location, may cause symptoms such as heavy or irregular menstrual bleeding, periods that last longer than normal, discomfort during sexual intercourse or subfertility and spontaneous abortions.Three out of four women will have fibroids at some point in their lives, but only one in four will experience symptoms:
Heavy menstrual bleeding
Irregular bleeding
Menstruation that lasts longer than normal
Feeling of weight in the lower abdomen
Need to urinate more often
Unusual constipation
Anemia
Discomfort during sexual intercourse
Hypofertility and miscarriage
Lumbar pain in the lower back if the fibroid is large
If uterine fibroids cause symptoms that affect the patient's daily activities or make it difficult to carry a pregnancy to term, myomectomy is the most appropriate surgical procedure, as it allows the fibroids to be removed, alleviates symptoms and preserves the uterus.
Types of myomectomies
Myomectomy or removal of uterine fibroids, depending on the size, location and quantity, can be performed by three access routes:
By the abdomen: Abdominal myomectomy.
Through the vagina and cervix: Hysteroscopic myomectomy.
Through small incisions at or very close to the navel: Laparoscopic myomectomy.
Abdominal myomectomy or laparotomy?
Abdominal myomectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing fibroids by making an open incision or incision in the lower abdomen, like a caesarean section, often horizontal and parallel to the waist, through which the surgeon accesses the uterus and proceeds to the practice of fibroid removal.
The procedure may require 2 to 3 days of hospitalization, and the recovery of the patient may require between 3 and 4 weeks of relative rest.
Hysteroscopic myomectomy or hysteroscopy
La myomectomie hystéroscopique est une intervention chirurgicale qui consiste à enlever les fibromes (sans incision ni coupe ouverte) à l'aide d'instruments ( hystéroscope ou résectoscope) qui sont passés dans l'utérus par le vagin et le col de l'utérus.
L'hystéroscope est équipé d'une lumière et d'une caméra avec lesquelles une image agrandie de l'intérieur de l'utérus est obtenue et affichée sur un écran. Les fibromes peuvent être retirés avec un hystéroscope, qui est utilisé pour retirer les fibromes de la paroi utérine à l'aide d'énergie électrique, ou avec un morcellateur hystéroscopique, avec lequel le chirurgien coupe manuellement le fibrome.
La myomectomie hystéroscopique est possible si les fibromes causés par les fibromes utérins sont de taille adéquate et dépassent suffisamment dans l'utérus.
Le patient sort généralement le jour même de l'intervention et le rétablissement du patient peut nécessiter environ 1 semaine de repos relatif.
Laparoscopic or laparoscopic myomectomy
Laparoscopic myomectomy is a minimally invasive surgical technique that allows the patient to intervene and remove uterine fibroids by making small incisions and without having to open the abdomen.
Laparoscopic surgery, which is a less invasive option than abdominal surgery, requires considerable experience, specialization and expertise from surgeons.
In a laparoscopic myomectomy, small incisions are made in or very close to the navel, through which surgical instruments and a tube with a small camera (the laparoscope) are inserted and the procedure is performed to remove the fibroids.
Single-port or single-port myomectomy is laparoscopic surgery that is performed through a single micro-incision in the abdomen (usually in the umbilicus) through which surgical instruments are inserted, including the camera which allows you to view the interior.
Robotic myomectomy is a robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery, a surgery particularly suitable for performing very complex surgical procedures. By means of robotic arms and articulated grippers, the robot moves in real time and with absolute fidelity the movements of the surgeon's hand.
The use of the robot offers the surgeon greater safety when treating hard-to-reach anatomical areas, facilitates a magnified view of the patient's interior, ensures stable handling of surgical instruments and allows maximum precision in the movements of the surgeon. hands.
The advantages and benefits of laparoscopic myomectomy, a minimally invasive surgery, compared to conventional open surgery are numerous:
Less postoperative pain.
Less medicine.
Less inflammatory reaction.
Less risk of infection.
Shorter hospital stay.
Much faster patient recovery.
Esthetic results often practically imperceptible.
Recovery from laparoscopic surgery is faster than that from abdominal myomectomy: the patient can be discharged the same day as the operation, and full recovery may require 2 to 3 weeks of relative rest, during which it is recommended avoid strenuous exercise.
Comment se preparer à l'intervention?
It is recommended that the patient reduce her stress in the days preceding the intervention, not to consume tobacco (as this can hinder postoperative recovery), not to drink alcohol during the 48 hours preceding the intervention, and to follow her gynecologist's instructions to maintain a soft diet.
It is essential that the patient informs her surgeon beforehand of the medications, supplements or natural remedies that she could take, so that he can indicate the procedure to follow in the days preceding the intervention.
How is a myomectomy performed?
Laparoscopic surgery is performed by painless small incisions through which a tube with a small camera (the laparoscope) is inserted, controlled by a second surgeon, which allows the inside of the abdomen to be viewed on a screen placed in the operating room itself and guiding the surgeon patient inside the body.
To perform laparoscopy, general anesthesia is usually applied.
Instead of opening (as in a cesarean), one or more small painless incisions are made very close from the navel.
Through the incisions, gas (carbon dioxide) is introduced to inflate the abdomen and provide space and visibility to the surgeon.
A tube with a small camera (the laparoscope) is placed through the incision.
Surgical instruments are introduced (forceps, scalpel and other very small devices) which allow the surgeon to manipulate in internally without having to open the abdomen.
The camera allows you to view the inside of the abdomen on a screen placed in the operating room.
When the procedure is complete, the incisions are closed with simple stitches and very often the patient released the same day of the intervention.
What does postoperative recovery look like?
Myomectomy recovery time varies depending on the approach:
Abdominal myomectomy. Being an open surgery, this therapeutic option is the one that requires the longest hospitalization and postoperative recovery time. Frequently, the procedure may require hospitalization for 2 to 3 days and recovery may take up to 3 to 4 weeks.
Hysteroscopic myomectomy. Once the hysteroscopic myomectomy is performed, the patient can be discharged the same day of the procedure, while postoperative recovery may involve approximately 1 week of relative rest, during which the patient is recommended to avoid strenuous exercise.
Laparoscopic myomectomy. Postoperative recovery from laparoscopic surgery, a non-invasive surgical technique, is much more comfortable and faster than conventional open surgery.The patient usually leaves the clinic the same day of the intervention, and postoperative recovery can last up to 2 or 3 weeks, during which it is recommended that the patient avoid strenuous physical exercise.