Gastric plication
Definition
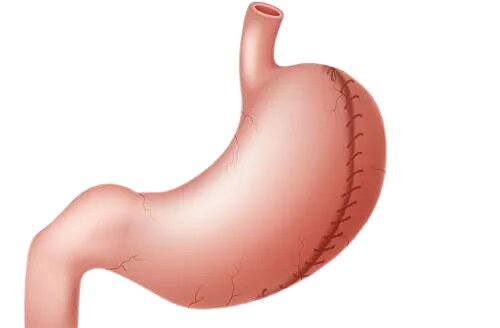 The gastric plication or stomach plication is performed through five or six small incisions in the abdomen and performing the procedure using a video camera (laparoscope) and long instruments that are placed through these small incisions. A continuous suture is applied to make large folds in your stomach.
The gastric plication or stomach plication is performed through five or six small incisions in the abdomen and performing the procedure using a video camera (laparoscope) and long instruments that are placed through these small incisions. A continuous suture is applied to make large folds in your stomach.
Who is a candidate?
Gastric plication surgery is relatively new, considered a premier procedure for weight loss . Surgery should be likened to sleeve gastrectomy. We do not yet have long-term results. The first results are encouraging, but we do not yet have enough experience to offer this intervention to many patients. Patients are included in a cohort follow-up to assess the results.
The process
During gastric plication, the volume is reduced by about 70% which makes the stomach able to contain less and can help you eat less. There is no cutting, stapling, or removal of the stomach or intestines during gastric plication. Gastric plication can potentially be reversible or converted to another procedure if necessary.
Gastric plication is a laparoscopic (laparoscopic) procedure, which is very simple and yet very effective. It is less invasive and shorter than the sleeve and the bypass (the operation lasts between 1 and 2 hours), while offering just as good results.
How does she lose weight?
Stomach plication is a restrictive procedure. It drastically reduces the size of your stomach and limits the volume of food that can be eaten at one time. It does not cause decreased nutrient absorption or short circuiting of your intestines.
After eating a small amount of food, you feel full very quickly and continue to feel full for several hours. Gastric plication can also cause a decrease in appetite.
There is no removal of part of the stomach. The latter is simply sewn inwards and sutures are used to reduce its size, just as a tailor would do to take up a dress or a pair of pants.
What are your BMI and IMG indexes ?
Tests to do before a Gastric plication
Blood group. Full blood count. Serum Urea. serum creatinine. Protidemia and protein electrophoresis. Serum electrolytes. Calcemia. Cholesterol. Triglycerides. HDL, VLDL. Low cortisol at 7 a.m. Thyrostimulin T4. FSH. LH.
Osogastroduodenal endoscopy.
Electrocardiogram - Cardiac Ultrasound.
Abdominal ultrasound.