Penile prosthesis
Defintion
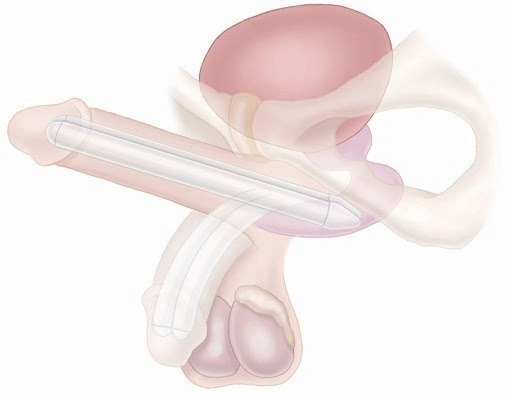 The penile prosthesis is a medical device surgically implanted in the erection chamber of the penis (corpus cavernosa) in the event of erectile dysfunction.
The penile prosthesis is a medical device surgically implanted in the erection chamber of the penis (corpus cavernosa) in the event of erectile dysfunction.
When to consider surgery?
If the use of the PDE5 inhibitor and the intracavernous injections did not bring positive results, the penile prosthesis could represent a valid option for the patient. Phalloplasty might be recommended if you cannot take PDE5 inhibitors or injection medications or if you are unhappy with the result and want a lasting solution.
How does the penile prosthesis work?
There are two types of implants:
Non-inflatable RIBs and inflatables.
The semi-rigid prosthesis consists of two cylinders that are implanted in the corpora cavernosa (the erection chamber of the penis) and which can be folded up during sexual activity. With this type of implant, the penis always remains in a semi-rigid position, a condition that is difficult to conceal.
Inflatable penile implants are devices that are filled with a liquid. The prosthesis consists of two inflatable cylinders placed in the corpora cavernosa of the penis, a manually operated pump placed in the scrotum, and a reservoir that retains fluid when the penis is not erect. The device inflates when the pump is pressed several times to allow fluid to move from the reservoir into the cylinders. At the end of the sexual intercourse, the pump is activated again to return the liquid to the reservoir, causing the erection to disappear.
Both prostheses are surgically implanted and fully positioned within the body. Inflatable implants are used more frequently because they provide more natural results. In more complex cases, semi-rigid implants may not be suitable. It is advisable to discuss which type to choose with your urologist.
Surgery
Penile implantation is performed under general or spinal anesthesia. The patient will be placed a catheter which will be removed the day after the surgery. Once the patient is anesthetized, the surgeon will make a small incision just above the penis or between the penis or the scrotum. The incision will show the corpora cavernosa and the surgical spaces in which to place the implant of the correct length.
Once the cylinders are in place, the reservoir is placed behind the abdominal wall and the pump is placed in the scrotum between the testicles and to conceal the pump.
When all the elements are implanted, they are connected together and the incision is sutured. The wounds are cleaned and a pressure bandage is applied. Most surgeons prefer to leave the penis implant inflated for a day. Others prefer to leave the drainage which is normally removed after the first day.
When to resume daily activities?
Normally, the patient can be discharged the day after the procedure after the dressing has been removed and the implant has been deflated by the surgeon. The patient may experience pain, irritation, swelling of the penis and scrotum in the days following the surgery or in the weeks that follow.
These symptoms can be treated with painkillers and cold compresses. In the first 2 or 3 days after surgery, there may be small discharge from the incision which does not need to be treated as it heals on its own.
For 4 to 6 weeks after surgery:
Do not lift more than 5 kg.
Don't exercise and avoid cycling.
Do not take thermal baths or saunas.
Discuss any medications you should be taking with your doctor.
The doctor will arrange an appointment to inflate the implant for the first time. This procedure will be performed once the swelling and irritation subsides, approximately 4 to 6 weeks after surgery. After this meeting, the patient can resume sexual activity.
You should tell your urologist if:
The swelling is getting worse instead of better.
There is a constant secretion of purulent fluids from the wounds.
Pain intensifies or does not improve.
You notice redness or tenderness in the incised area.
Fever occurs.
Advantages
Reduced likelihood of mechanical failures.
Possibility to inflate the device discreetly.
Inflatable implants can be easily hidden.
No risk of priapism.
The most satisfactory result among the possible treatments.
Highest percentage of satisfied patients in all ED therapies when informed, including partners , on various aspects of the implant.
Disadvantages
Irreversible operation.
If the device is removed, there is no way to recover erectile function.
Risk of infection, albeit minimal.
Risk of device failure, however minimal.
Usually the swelling implant takes 10-15 years. It will be possible to replace the device in case of failure.
Minimal rate of uncontrolled bleeding after the operation. In this case a second intervention will be necessary.
Minimum percentage of abnormal scar tissue formation.
Minimum erosion percentage, which may require elimination.
The glans may not grow during an erection.
The implant may not swell the penis or correct previous length loss, whether due to prostatectomy, radiation therapy, aging, weight gain, or long-term treatments for erectile dysfunction.