thoracotomy Tunisia
What is a thoracotomy?
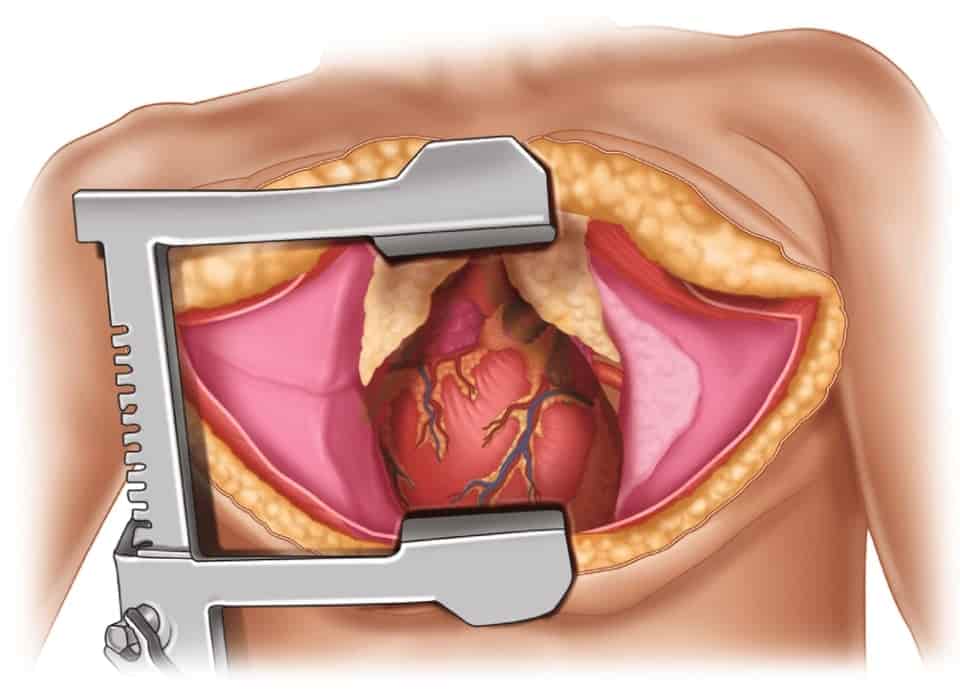 The chest wall is incised during a major surgical procedure known as a thoracotomy. It is performed by a thoracic surgery professional and provides access to organs such as the heart, lungs, esophagus and thoracic aorta, as well as the internal part of the spine. Lung and heart diseases can be treated with this procedure, which may be included in a number of other thoracic surgical procedures. Lobectomy and pneumonectomy, which are the most common treatments for lung cancer, are some of the many reasons thoracotomy may be performed.
The chest wall is incised during a major surgical procedure known as a thoracotomy. It is performed by a thoracic surgery professional and provides access to organs such as the heart, lungs, esophagus and thoracic aorta, as well as the internal part of the spine. Lung and heart diseases can be treated with this procedure, which may be included in a number of other thoracic surgical procedures. Lobectomy and pneumonectomy, which are the most common treatments for lung cancer, are some of the many reasons thoracotomy may be performed.
What are the stages of the thoracotomy surgical process?
The chest wall is incised during a major surgical procedure known as a thoracotomy. It is performed by a thoracic surgery professional and provides access to organs such as the heart, lungs, esophagus and thoracic aorta, as well as the internal part of the spine. The stages of thoracotomy are as follows:
Preparation for the procedure: The patient's state of health, the nature of Lung disease, patient and medical team preferences influence the decision to proceed with thoracotomy.
Incision: Normally, the incision is made around the shoulder blade, with a opening between ribs 5 and 6 and the posterior section of the 6th rib if necessary.
Exposure of structures: The structures of the thorax, such as the bronchi, diaphragm, the esophagus and thoracic aorta, can be exposed during thoracotomy.
Resection of pathological structures: Pathological structures, such as a lung lobe ( lobectomy), the entire lung (pneumonectomy) or others, may be resected depending on the nature of the lung disease.
Suture and drainage: To prevent the accumulation of air, blood and serosities in the chest cavity, the structures are sutured and pleural drainage is generally put in place.
Recovery: Recovery after a thoracotomy can last several weeks to several months, depending the patient's state of health and the nature of the lung disease.
How is recovery after surgery?
Recovery after thoracotomy surgery can vary depending on a variety of factors, including the health of the patient, the nature of the lung disease, and the possibility of complications. Pain after thoracoscopy is usually a little more painful than after surgery, and hospitalization usually lasts between 2 and 6 days. People with persistent pain require specific treatment.
The patient is generally monitored in the recovery room after surgery before returning to their room. Regional anesthesia is used to treat postoperative pain in different ways. Chronic neuropathic pain may persist later and require more treatment.
When there is a complication, recovery may take longer and require more treatment. For example, recovery may be prolonged and require additional treatment if there is a reaction to anesthesia, infection, bleeding, injury to the adjacent abdominal organ, or other complications.
What are the advantages ?
The benefits of thoracotomy vary depending on the lung disease and the surgical method used. To treat certain lung diseases, such as lung cancer, thoracotomy is generally considered an effective surgical procedure. Thoracotomy can reduce symptoms of lung disease such as cough, shortness of breath and chest pain. Additionally, thoracotomy may benefit lung cancer patients because it removes tumors and, in some cases, increases survival.
What are the possible complications of the surgery?
Although potential complications of thoracotomy are rare, the following may be included:
Infections: After thoracotomy, infections, including lung infections, pneumonia or Ear infections may develop.
Respiratory failure: The complication of thoracotomy can be respiratory failure, in particular if healthy lung tissue is removed.
Hemorrhage: After a thoracotomy, it is possible that hemorrhage may occur, particularly if healthy lung tissue is extracted.
Bronchopleural fistula: An abnormal communication between the bronchial tree and the pleura, which can develop after a thoracotomy, is known as a bronchopleural fistula.
Pericardial effusion: A complication of thoracotomy can be pericardial effusion, particularly if healthy lung tissue is removed.
Rib fractures: After a thoracotomy, it is possible to develop rib fractures , especially if healthy lung tissue is removed.
Persistent pain: After thoracotomy, pain may persist and pain medication is generally recommended. recommended for two months.
What is the typical duration of a thoracotomy?
Several factors, including the nature of the lung disease, the patient's medical condition, and the surgical technique used, determine the typical duration of a thoracotomy. The procedure generally lasts between 2 and 3 hours. Before entering their room, the patient is generally monitored for a few hours in the recovery room.
What are the expected results ?
The expected results of a thoracotomy vary depending on the lung disease and the surgical technique used. Thoracotomy is generally used to treat pulmonary and cardiac pathologies, and in more than 90% of cases, it can help identify a lung disorder because it allows careful visualization of the sampling site and obtaining tissue for examinations. under a microscope.
How long does recovery take after surgery?
Recovery time after a thoracotomy can vary depending on a variety of factors, including the nature of the lung disease, the patient's health, and the possibility of complications. The patient can usually expect a hospitalization of several days, usually between 5 and 7 days. Regional anesthesia and pain medications are used to manage postoperative pain. Chronic neuropathic pain may not go away later and may require additional treatment. Respiratory physiotherapy also begins early to help the patient breathe correctly and prevent bronchial congestion. The patient can gradually return to physical activity after a month and if there have been no complications.
Are there any alternatives to this surgery?
To treat certain lung diseases, there are alternatives to thoracotomy. These options include:
Thoracoscopy: Another surgical method that provides access to lung structures is thoracoscopy . Lobectomies (resection of a lobe of the lung) and pneumonectomies (resection of an entire lung) are two procedures for which it is frequently used.
Sternotomy: A surgical procedure called a sternotomy involves an incision through the breastbone to access the lung. It can be used as an alternative to thoracotomy for the excision of upper lobe tumors.
Mediastinoscopy: A minimized technique called mediastinoscopy allows access to lung structures through an incision in the anterior part of the thorax, between the sternum and the diaphragm. Lobectomies and pneumonectomies can be performed there.
What are the criteria to be eligible for a thoracotomy?
Eligibility criteria for a thoracotomy vary depending on the type of lung disease and the surgical method used. Treatment of lung and heart disease involves a major chest surgery called a thoracotomy. It can be performed as part of various thoracic surgical procedures. The surgeon determines eligibility criteria based on the patient's health, the nature of the lung disease, the preferences of the patient and the medical team.
What is the success rate?
Several factors influence the success rate of thoracotomy, including the nature of the lung disease, the patient's health status, and the surgical technique used. To treat certain lung diseases, such as lung cancer, thoracotomy is generally considered an effective surgical procedure. Thoracotomy can reduce symptoms of lung disease such as cough, shortness of breath and chest pain.
It is important to note that results may differ depending on the nature of the lung disease, the patient's health status and individual response to treatment. Currently, the rate of postoperative complications is estimated between 5 and 10%. Approximately 95% of patients undergo thoracoscopy successfully.
Are there any long term side effects?
Long-term side effects of thoracotomy may include persistent pain, respiratory problems, lung infections, hemorrhage, bronchopleural fistulas, pericardial effusions, and rib fractures. Nerve damage or scarring can cause chronic pain that may persist for several months or years after surgery. Decreased lung capacity can lead to breathing problems, especially if healthy lung tissue is removed. After a thoracotomy, lung infections can occur, particularly if healthy lung tissue is removed. Although other potential complications of thoracotomy are rare, they can affect the patient's recovery and quality of life.
How long does one live after a thoracotomy?
Lifespan after thoracotomy depends on many factors, including the nature of the lung disease, the patient's health status, and individual response to treatment.