Varicocele Tunisia
Definiion
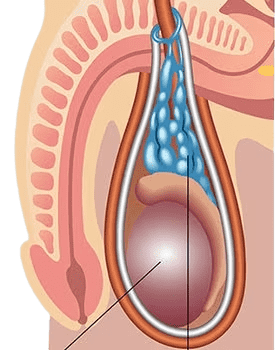 Varicoceles are an abnormal enlargement of the veins in the scrotum, the pocket of skin that contains the testicles in men. These dilated veins are similar to varicose veins found in the legs, and can cause pain and a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum.
Varicoceles are an abnormal enlargement of the veins in the scrotum, the pocket of skin that contains the testicles in men. These dilated veins are similar to varicose veins found in the legs, and can cause pain and a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum.
Varicoceles can affect male fertility by disrupting sperm production and increasing the temperature in the testicles, which can affect sperm quality. Varicoceles are quite common in men and can be treated if necessary.
What are the causes ?
The exact causes of this dilation are not completely understood, but it may be related to a combination of factors.The main possible causes of varicocele are:
Abnormalities in the testicular venous valves, which control blood flow through the veins and ensure the return of blood to the heart .
Abnormalities in the structure of the testicular veins, which can cause venous insufficiency.
Genetic or hereditary factors, which may favor a predisposition to develop a varicocele.
Environmental factors, such as prolonged exposure to heat in the genital area, which can increase testicular temperature and affect blood circulation.
It should be noted that although the environmental factor may be a cause, it is often not the only or even the main factor responsible for varicocele.
What are the symptoms ?
Common symptoms of varicocele can include:
A lump or swelling in the scrotum.
Mild to severe pain in the scrotum, which may increase with prolonged activity, especially when standing or seated.
Feelings of heaviness or pulling in the scrotum.
Decreased ejaculate volume.
Visible varicose veins in the scrotum.
Infertility (in some cases).
How is it diagnosed ?
Varicocele can be diagnosed by a doctor using a physical exam and a Doppler ultrasound exam.
During the physical exam, the doctor will examine the scrotum and testicles for any lump or swelling. He may also ask you to cough to assess whether the swelling in the testicle is going down or not. If this occurs, it may indicate a varicocele.
Doppler ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of blood flow through blood vessels. It can help confirm the diagnosis of varicocele and determine its stage.
Can it cause male infertility ?
Yes, varicocele can cause male infertility in some men by affecting the quality and quantity of sperm produced. Varicose veins that form in the veins that drain the testicles can contribute to blood pooling in the testicles and raising their temperature, which negatively affects sperm production.
About 40% of men with varicocele experience infertility or a decline in the quality of their sperm. However, this does not necessarily mean that varicocele will cause infertility in all men who suffer from it. Some men can have a varicocele without any symptoms or effects on their fertility.
If a man with varicocele is having difficulty conceiving a child with his partner, it is recommended to consult a doctor to assess the possibility that varicocele is a contributing factor.
What are the types ?
Risks associated with profiloplasty can include bleeding, infection, pain, bruising, swelling, scarring, asymmetries, sensory disturbances, breathing problems, healing problems, and unsatisfactory results. However, these risks are generally rare and can be minimized by following postoperative instructions, and taking care of your health before and after the procedure.
What are the possible treatments ?
There are several treatment options for varicocele. Common treatments include:
Observations: If the varicocele is mild or does not cause symptoms, the doctor may simply recommend observation of the varicocele. condition and schedule regular check-ups to monitor any changes.
Surgery: Surgery, called varicocelectomy, is the most commonly used treatment for varicocele. It is performed under general anesthesia and aims to remove or ligate dilated veins, in order to improve venous blood flow to the testicles. The surgery can be performed through different techniques, including the traditional open procedure, microsurgery, and laparoscopy.
Embolization: Embolization is a procedure involving the insertion of a catheter into a vein in the groin to inject a sclerosing substance which obstructs the dilated veins. This leads to a decrease in pressure in the affected veins and restores normal blood flow. Embolization is a less invasive alternative to surgery.
The choice of treatment depends on several factors, such as the age of the patient, the severity of the varicocele, and the presence of symptoms. However, it is important to talk with a doctor to find the treatment that is best for each individual case.
Embolization
This procedure is performed using medical imaging techniques to guide the radiologist in inserting a blocking agent into the diseased spermatic vein. Varicocele embolization is an alternative to surgery for treating varicoceles, which are swollen veins in the scrotum that can cause pain, infertility, and swelling. The risks of varicocele embolization are rare, but may include infection, allergic reaction, excessive bleeding, or migration of the blocking agent.
How is the surgery performed ?
Varicocele surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia and consists of ligating or cutting the dilated veins of the spermatic cord that cause the varicocele. Here are the main steps of the intervention:
Anesthesia: The patient is asleep under general anesthesia.
Access to the area: The surgeon makes a small incision in the groin or abdomen area to access the dilated veins of the spermatic cord.
Ligation or section of veins: The surgeon ligates or cuts dilated veins for abnormal blood reflux and improves blood flow in normal spermatic veins.
Closing the incisions: The surgeon closes the surgical incisions with stitches or surgical tape.
Recovery: After the procedure, the patient should stay at the clinic for monitoring and to recover. Most patients can go home the day of surgery or the next day. The patient should follow the medical team's instructions regarding post-operative care, such as prolonged rest, use of testicular support, taking painkillers, and heavy physical activity restrictions.
Varicocele surgery is considered a safe and effective procedure to reduce varicocele symptoms and improve male fertility in patients with varicocele.
Is it painful ?
The pain associated with varicocele surgery can vary from person to person and will also depend on the surgical technique used. However, most patients report some pain after the procedure, which can be managed with pain medication.
Varicocele surgery can be performed under general or local anesthesia, depending on patient and surgeon preference. After surgery, there may be mild to moderate pain in the incision area or in the scrotum, which may last for a few days to a few weeks. However, most patients can resume normal activities within a few days.
How long does it take to recover ?
Recovery time after varicocele surgery depends on several factors, such as the extent of the surgery, the age and general health of the patient, and the surgical technique used. In general, most patients fully recover within 2-4 weeks after surgery.
Here is a rough estimate of the stages of recovery after varicocele surgery:
1-2 weeks: Following surgery, the patient may experience mild to moderate pain, bruising and tenderness. swelling in the groin area or testicles. It is generally recommended to avoid strenuous physical activities and to wear a testicular support to support the testicles and avoid sudden movements. 2-3 weeks: The pain and bruising gradually decreases, and the patient may begin to gradually increase their level of pain. physical activity according to the surgeon's recommendations.
4+ weeks: Most patients can return to their normal activities about 4 weeks after surgery.
Are there any associated complications ?
Complications are generally rare and the procedure is considered safe and effective. Here are some potential complications associated with varicocele surgery:
Hematoma: Excessive bleeding can cause a hematoma, a pocket of blood that forms under the skin. This complication can cause pain and swelling in the groin area or testicles.
Infection: There may be a slight possibility of infection after surgery, although this is also rare. Signs of infection include increased pain, redness, swelling, and fever.
Reappearance of varicocele: There is a possibility that varicocele may recur after surgery, especially if the surgical technique used is ineffective.
Accidental injury to surrounding blood vessels, nerves or organs: Although this is also rare, there is a risk of accidental injury to surrounding tissues during surgery.
Can it come back after surgery ?
It is possible for varicocele to come back after surgery, but this is quite rare. Success rates for varicocele surgery vary depending on the surgical technique used, the experience of the surgeon, and the severity of the condition. Success rates generally vary between 85% and 95%.
Factors that may increase the chances of the varicocele coming back after the operation include:
Incorrect or improper surgical technique used.
A grade III or IV varicocele before surgery.
Chronic venous insufficiency or vascular obstruction.
Patient non-compliance with postoperative restriction instructions.