Adenoids adults and children
What are adenoids in adults and children?
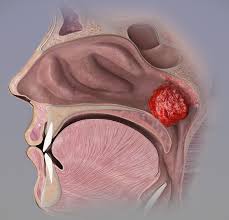 The adenoids, also called pharyngeal tonsils, are lymphoid tissues located in the back of the throat, near the palatine tonsils, in children and adults. They are part of the lymphatic system, which plays a role in the body's immune defense.
The adenoids, also called pharyngeal tonsils, are lymphoid tissues located in the back of the throat, near the palatine tonsils, in children and adults. They are part of the lymphatic system, which plays a role in the body's immune defense.
In children:
Adenoids are naturally larger in young children and begin to shrink from the age of 5 . They reach their maximum size around the age of 5 to 7 years.
Adenoids are an important part of children's immune systems and help fight infections.
In some children, the adenoids may become enlarged, causing symptoms such as breathing problems, snoring, recurrent ear infections and upper respiratory infections. In these cases, an adenoidectomy (removal of the adenoids) may be considered.
In adults:
In adults, the adenoids naturally regress and become much smaller than in children.
Adults generally have non-enlarged adenoids, and they are less likely to cause health problems.
Symptoms of enlarged adenoids, such as difficulty breathing, snoring and infections, are more common in children than in adults.
When do adenoids reach their maximum size in children?
Adenoids reach their maximum size between two and six years of age. Adenoids naturally diminish and disappear in older adolescents after this age. It should be noted that in some children, the adenoids may be constitutionally enlarged, which can lead to nasal obstruction, snoring and sleep apnea. In this case, it may be necessary to remove them surgically.
What are the symptoms of enlarged adenoids in children?
Enlarged adenoids in children can cause the following symptoms:
Difficulty breathing normally through the nose.
Snoring.
Insomnia.
Night terrors.
Enuresis.
Faulty pronunciation.
Sonorous voice.
Abnormal palate shape and position of teeth.
Tendency to breathe through the mouth.
Weight loss or insufficient weight gain.
Do adults have adenoids?
Lymphoid tissues called adenoids are found behind the nasal cavity, in the nasopharynx or cavum. Although rare, adenoids can be present in adults. Adults with enlarged adenoids may have symptoms similar to children, such as difficulty breathing normally through the nose, snoring, insomnia, a ringing voice, and weight loss or insufficient weight loss. The ENT surgeon gives the indication to remove the adenoids, also called "adenoidectomy". If symptoms are present, the intervention is carried out from 1 year until puberty. Symptoms of adenoid enlargement in adults should be discussed with their doctor.
What are the health problems related to adenoids in adults?
Health problems related to adenoids in adults are rare, but may include the following symptoms:
Difficulty breathing normally through the nose.
Snoring.
Insomnia.
Sonorous voice.
Weight loss or insufficient weight gain.
How is an adenoidectomy performed in children?
Here is the information on the procedure of an adenoidectomy in children:
An adenoidectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing adenoids in children.
The operation is carried out under general anesthesia, that is to say the child will be asleep.
The operation consists of removing the adenoids through the mouth, by means of cauterization and suction.
The operation lasts approximately 20 minutes.
Adenoidectomy may be performed on an outpatient basis or the child may have to stay overnight in the hospital. observation purposes.
After surgery, many children have headaches, throat pain, neck pain, jaw or ears. Children may also experience pain or discomfort in their throat, ears, and mouth.
When is it necessary to perform adenoidectomy in adults?
In adults, adenoidectomy is a rarely performed surgical procedure because adenoids tend to shrink and disappear with age. However, in rare cases, an adenoidectomy may be necessary in adults to treat health problems such as:
Chronic nasal obstruction.
Chronic infections of the upper respiratory tract.
Snoring and sleep apnea.Adenoidectomy in adults is performed under general anesthesia, and the operation involves removing the adenoids through the mouth, by means of cauterization and suction.