patella fracture
Definition
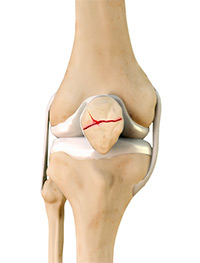 The patella fracture generally occurs during a direct impact or a fall on the knee. The clinical signs are pain, inability to mobilize the knee, swelling of the knee due to bleeding in the joint. The X-ray confirms the clinical diagnosis. The patella is attached to the skeleton by two tendons: the quadriceps tendon and the patellar tendon. During a transverse fracture, the upper fragment is often ascended by the contraction of the quadriceps.
The patella fracture generally occurs during a direct impact or a fall on the knee. The clinical signs are pain, inability to mobilize the knee, swelling of the knee due to bleeding in the joint. The X-ray confirms the clinical diagnosis. The patella is attached to the skeleton by two tendons: the quadriceps tendon and the patellar tendon. During a transverse fracture, the upper fragment is often ascended by the contraction of the quadriceps.
Orthopedic treatment
The indication for orthopedic treatment of the knee fracture is the absence of displacement and the stability of the fracture. A knee brace is applied. Support is authorized but flexion of the knee is prohibited for a month and a half. preventive anticoagulant treatment is instituted during this period. After consolidation, the splint is removed and rehabilitation to regain knee mobility is started.
The surgical procedure
The patella fracture is most often displaced and comminuted, it then requires surgical treatment by osteosynthesis. The procedure takes place in the operating room in the orthopedic room under strictly aseptic conditions. The patient received the usual skin preparation in the room before being taken to the operating room. The patient is placed on his back on the operating table. After the usual skin preparation in the operating room, the sterile drapes are placed. The incision is made opposite the patella so as to visualize it in full. The surgeon reduces the fracture, places several pins and then performs a cerclage to stabilize everything.
Operative follow-up
Support is allowed but knee flexion is prohibited for a month and a half, under cover wearing a knee splint. A preventive anticoagulant treatment is instituted during this period. After consolidation, the splint is removed and rehabilitation to regain knee mobility is started. The osteosynthesis material will be removed 9 to 12 months later.