Hydrocele Tunisia
What is hydrocele ?
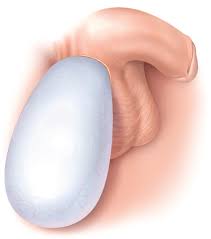 The hydrocele manifests itself by the presence of fluid in the testicular wall, which causes an almost permanent expansion of the scrotum. This accumulation of fluid can be observed in one or both testicles. Hydrocele is quite common in infants, but can also affect adults.
The hydrocele manifests itself by the presence of fluid in the testicular wall, which causes an almost permanent expansion of the scrotum. This accumulation of fluid can be observed in one or both testicles. Hydrocele is quite common in infants, but can also affect adults.
What are the causes ?
Hydrocele can have different origins depending on age and circumstances. Adults may experience hydrocele due to trauma, infections in the scrotum, testicle, or epididymis, obstructions in the spermatic cord, inguinal hernia operations, or even cancer. On the other hand, in infants and young children, hydrocele is frequently associated with patent peritoneal-vaginal canal, a congenital disturbance that facilitates the movement of fluid from the peritoneum into the colon.
What are the symptoms ?
Hydrocele is manifested by an increase in the volume of the scrotum, whether unilateral or bilateral, which can cause variable discomfort due to enlargement, a feeling of heaviness of the scrotum, pain in the testicles, discomfort and sometimes an aesthetic problem, especially during sexual intercourse.
How is it diagnosed ?
Typically, a doctor diagnoses hydrocele by performing a thorough clinical examination of the testicles, followed by an ultrasound to confirm the presence of fluid around the testicle. The clinical examination consists of observing and palpating the scrotum in order to identify a specific swelling. In addition, sometimes a special method called "transillumination" is used, which involves shining a flashlight into the scrotum to see if the light is entering the fluid cavity. The presence of a hydrocele is confirmed when light passes, while the absence of light passage may suggest other causes such as a herniation or testicular injury.
Can it cause male infertility ?
Indeed, hydrocele can be linked to infertility in men. In some situations, male infertility may result from obstruction of the male genital tract or injury, which may include conditions such as hydrocele that disrupt the production or release of sperm, contributing to sperm loss. male infertility.
What are the differences between hydrocele and other scrotal conditions ?
Hydrocele and other scrotal conditions are distinguished by their nature and their own particularities. Here are some significant differences:
The hydrocele is manifested by the presence of accumulated fluid between the layers of the tunic vaginal which covers the testicle. It can be seen as a painless swelling of the scrotum, without having an impact on the size of the testicle itself. It is possible for the hydrocele to be unilateral or bilateral and is usually benign. Its diagnosis can be established by palpation, transillumination and ultrasound.
varicocele is characterized by an increase in the size of the veins of the spermatic cord. Unlike hydrocele which is characterized by an accumulation of fluid, varicocele focuses on an expansion of blood vessels. Sometimes it can be linked to fertility difficulties in men.
spermatocele, another scrotal disease, manifests itself as an accumulation of sperm in the testicle or epididymis. Unlike the hydrocele which contains fluid, the spermatocele is characterized by sperm production. It can be diagnosed by performing a clinical examination and an ultrasound.
To recap, hydrocele stands out from other scrot conditions by emitting fluid between the layers of the tunica vaginalis, being painless, and being diagnosed using specific methods like transillumination and ultrasound .
What are the possible treatments ?
Possible treatments for hydrocele mainly include surgery. Hydrocele is treated by removing the sac that contains the fluid accumulated in the testicular wall. Typically, this procedure is simple and the prognosis is generally favorable. It should be emphasized that the use of puncture or injection of sclerosing product to treat hydrocele is not recommended due to the high risk of recurrence and infections. The surgery is carried out under general or loco-regional anesthesia, and it consists of making an incision in the scrotum in order to remove the fluid, as well as possibly resecting or plicating the membrane responsible for the hydrocele to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Is it possible for the hydrocele to disappear spontaneously ?
Indeed, it is possible that the hydrocele disappears spontaneously, particularly in male infants. About 10% of male infants and infants have hydrocele, which tends to resolve frequently without the need for specific treatment during the first year of life.
How is the surgery performed ?
Hydrocele surgery, also known as hydrocele treatment, is usually performed under general anesthesia on an outpatient basis. Here are the different common steps of this operation:
An incision and removal of the hydrocele is performed under general anesthesia, bypassing the hydrocele. Then the hydrocele is filtered and removed. The testicular vaginal membrane, which is responsible for the hydrocele, is resected or plicatured in order to reduce the risk of recurrence.
The different envelopes surrounding the testicle are closed and the skin is sutured with absorbable thread.
After the procedure, the absorbable sutures usually fall off on their own for about 2 to 3 weeks. Immediate problems that may arise after surgery may include scar infections and compartment hematomas.
After the procedure, recovery may require temporary rest and local care for a period of a few days to a few weeks, depending on the patient's individual reaction.
It is advisable to have regular medical follow-up in order to monitor healing and guarantee the absence of complications after the operation.
If the hydrocele recurs, it may be necessary to perform further surgery in order to effectively treat the condition.
Is the surgery painful ?
Thanks to anesthesia, hydrocele surgery usually involves no pain during the procedure. However, it is possible to feel postoperative pain after the operation, but this is generally alleviated thanks to analgesic treatments adapted to each situation. So, although some pain may occur after the procedure, it is usually controlled and gradually diminishes after the procedure.
How long does it take to recover ?
In general, it is advisable to allow a rest and recovery period of approximately 2 to 3 months after hydrocele surgery. During this period, it may be necessary to take local care for a few days, and it is common to notice swelling of the scrotum which may require additional rest. As a general rule, the bursa returns to its usual volume in 2 to 3 months after complete healing. It is also recommended to opt for sturdy underwear in order to preserve the bursae during the treatment period.
Work stopping ?
Following hydrocele surgery, it is advisable to take a few days off work. The precise duration may differ depending on the nature of the procedure, the patient's individual reaction and the specific recommendations of the treating physician. Generally speaking, it is common to prescribe a short period of time off work to allow the patient to rest and recover properly after the operation.
How to prevent recurrence after treatment ?
To prevent the hydrocele from returning after treatment, it is essential to follow the post-operative instructions given by the doctor. These actions may include:
It is best not to do strenuous physical activities during the recovery period.
Be sure to follow local care and hygiene instructions to avoid infection.
It is recommended to avoid baths for a period of time after the procedure.
It is important to strictly follow the instructions regarding prescribed medications.
If unusual symptoms occur, it is important to monitor carefully and report any concerns to your doctor immediately.
By following this advice and observing regularly with the attending physician, it is possible to considerably reduce the risk of recurrence of hydrocele after surgery.
What are the non-surgical treatments for hydrocele ?
Hydrocele has limited non-surgical treatments, and there are no effective medical solutions to treat it. Typically, surgery is the primary method of treatment for a hydrocele that persists or has symptoms. However, sometimes at-home solutions such as wearing supportive underwear or using cold compresses can temporarily relieve hydrocele discomfort. It is essential to seek the advice of a health specialist in order to obtain a precise diagnosis and advice adapted to each particular situation.